To provide examples on how the web server can be used for protein binding site prediction, we illustrate some case studies used to analyse protein-drug interactions in different perspectives.
Acarbose is indicated for diabetes and is known to inhibit alpha glucosidase. Inhibition of alpha glucosidase slower down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates thus reducing blood glucose concentration (https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00284). Acarbose may bind to multiple protein targets such as maltase glucoamylase, lysosomal alpha glucosidase, sucrase isomaltase and alpha amylase.
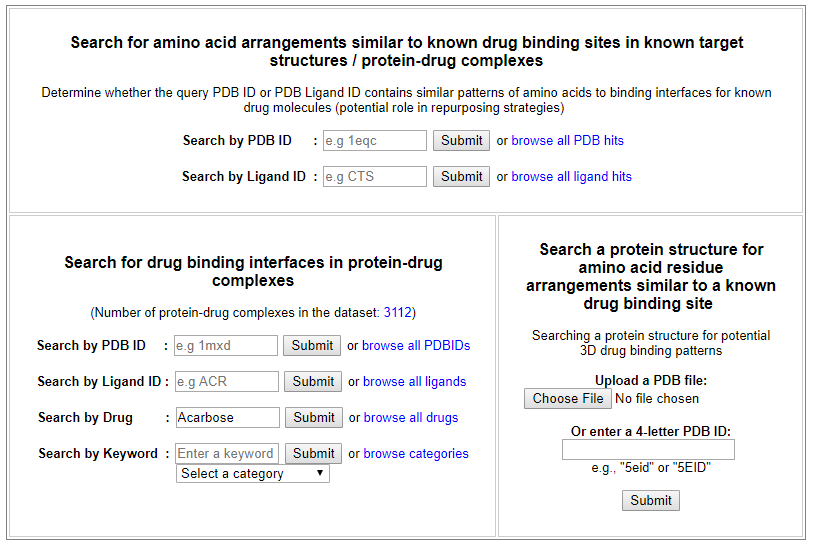
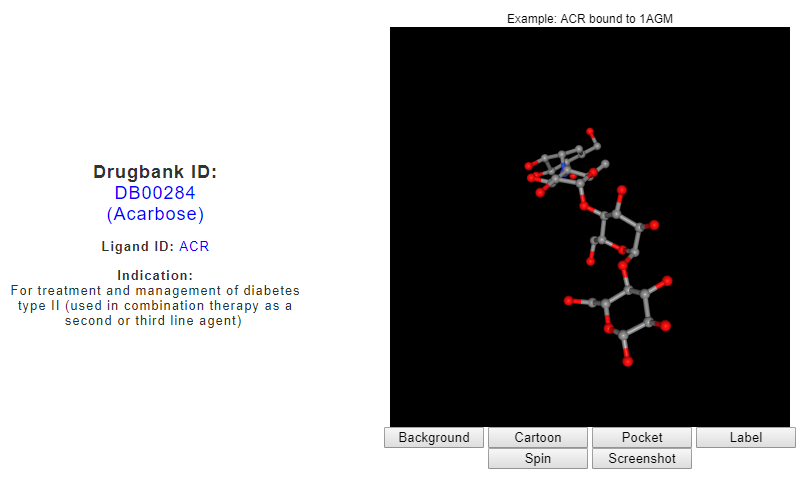
From the ‘Search for drug binding interfaces in protein-drug complexes’ interface, drug search for ‘Acarbose’ returns the drug indication as retrieved from the Drugbank, a visualization of PDB structure for Acarbose molecule (PDB ligand ID: ACR or QPS), and a list of known binding sites for Acarbose derived from the PDB.
The list returns binding sites for PDB ligand ACR and QPS, which are the two stereoisomers of Acarbose. By screening through the list, we can know that Acarbose binds to multiple targets based on different macromolecule name and Pfam annotation indicated in the fifth and sixth column, respectively. Some of the Pfam annotations involved include;
Glyco_hydro_15, Alpha-amylase, Glyco_hydro_31 and Glucodextran_N.
(Link)
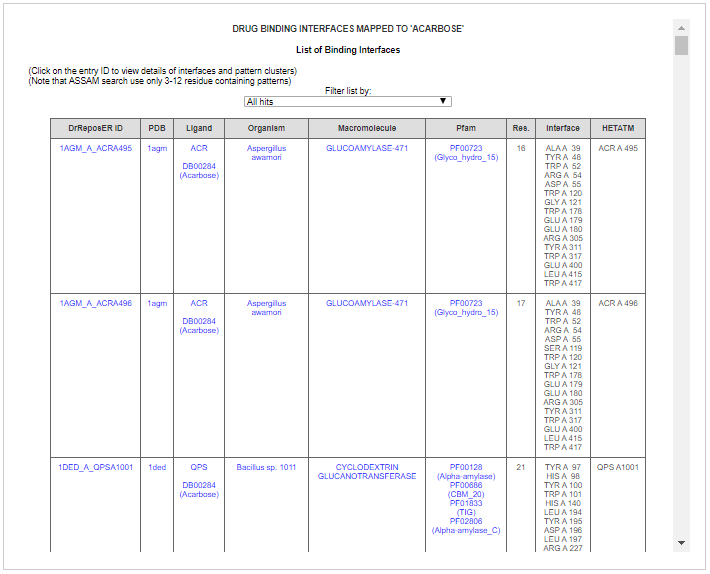
One of the binding sites is from an alpha amylase from Pyrococcus woesei (PDB ID: 1mxd) that contains 12-residue pattern surrounds an Acarbose molecule.
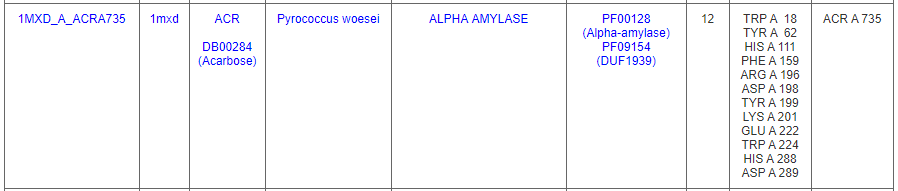
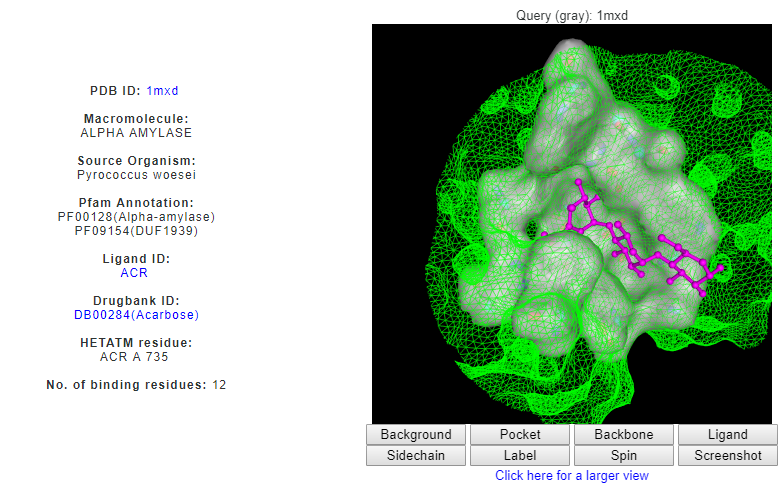
Clicking on the DrReposer ID '1MXD_A_ACRA735' returns a new page for similar patterns of amino acids predicted from the ASSAM search. User may sort the results according to RMSD, Z-score or sequence identity values.
(Link)
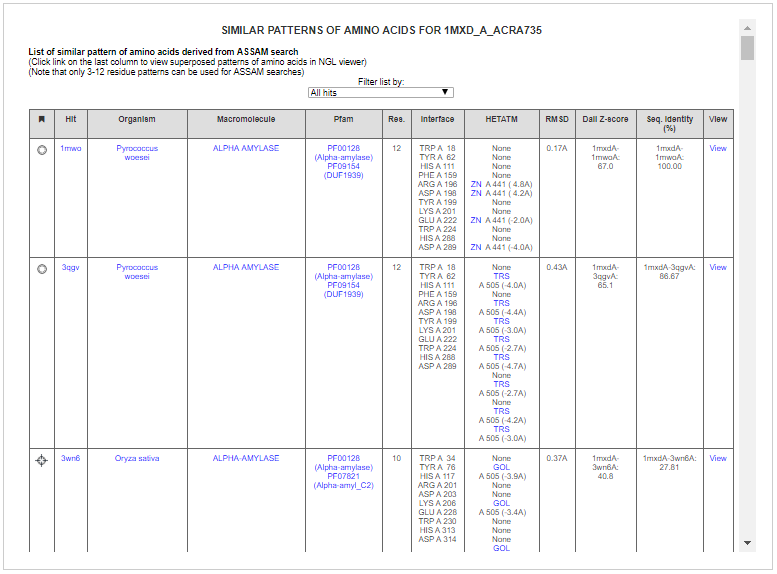
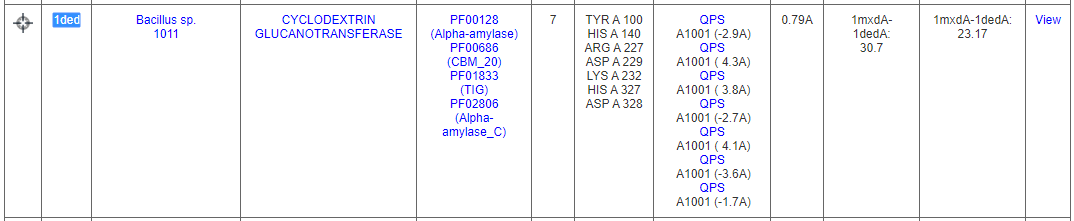
Some of the hits include related alpha amylases and gluconotransferases. ASSAM search found matched 7 residues that are similarly arranged as the query binding site from cyclodextrin glucanotransferase from Bacillus sp. (PBD ID: 1ded). The residues are found to be at the vicinity of an acarbose molecule (PDB Ligand ID: QPS).
Upon clicking the ‘View’ link on the last column, matched pattern of amino acids is shown in green, which is superposed to the query binding site (grey). Superposed ligand can also be seen, i.e. hit ligand is indicated in white, by clicking the 'Ligand' button on the NGL viewer. Ligand ID QPS can be seen to be well-superposed to its stereoisomer, ACR.