
To provide examples on how the web server can be used for protein binding site prediction, we illustrate some case studies used to analyse protein-drug interactions in different perspectives.
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) is a large protein family of transmembrane proteins with diverse functions. The proteins are diverse in sequence and function and can be further separated into different groups. The rhodopsin-like GPCRs (Pfam family '7tm_1') consists of a set of proteins including hormones, neurotransmitters and receptors which mostly involve with small molecule binding. GPCRs, or 7-transmembrane (7-TM) receptors are important drug targets, with more than 30% of FDA-approved drugs are bound to these proteins.
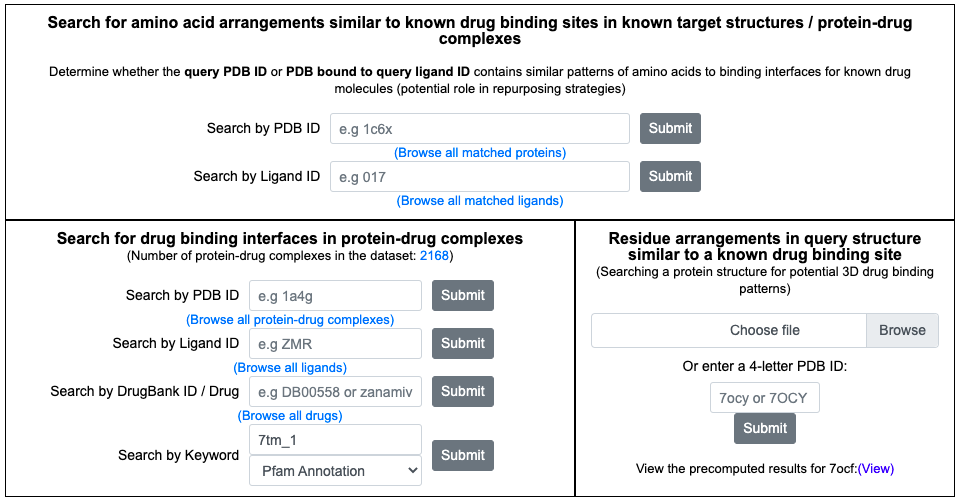
From the ‘Search for drug binding interfaces in protein-drug complexes’ interface, keyword search for ‘7tm_1’ under 'Pfam annotation' category returns a list of known binding sites from proteins with Pfam annotation '7tm_1' or PF00001. User may sort the list based on ligand name or number of residues.
(Link)
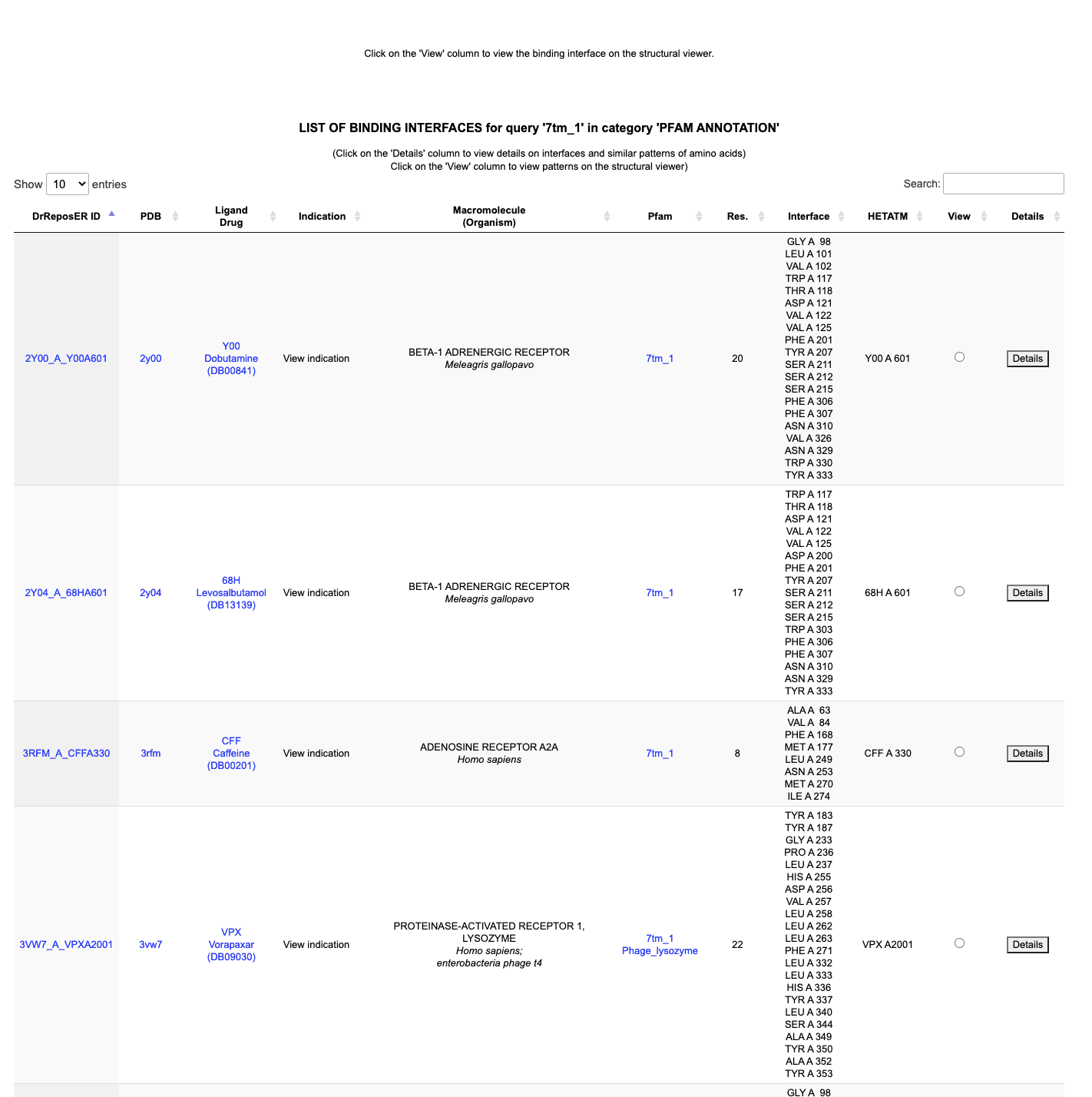
The fifth column ('Macromolecule name') shows the macromolecule name of the protein structure as derived from the PDB. Scanning through the column, the '7tm_1' keyword search mapped to different structures, such as adrenergic receptor, muscarinic acetylcholine receptor and adenosine receptor.
The third column ('Ligand') shows drug molecule that are bound to respective receptors. Scanning through the column, GPCRs can bind to different drug molecules, such as Caffeine and Dobutamine.
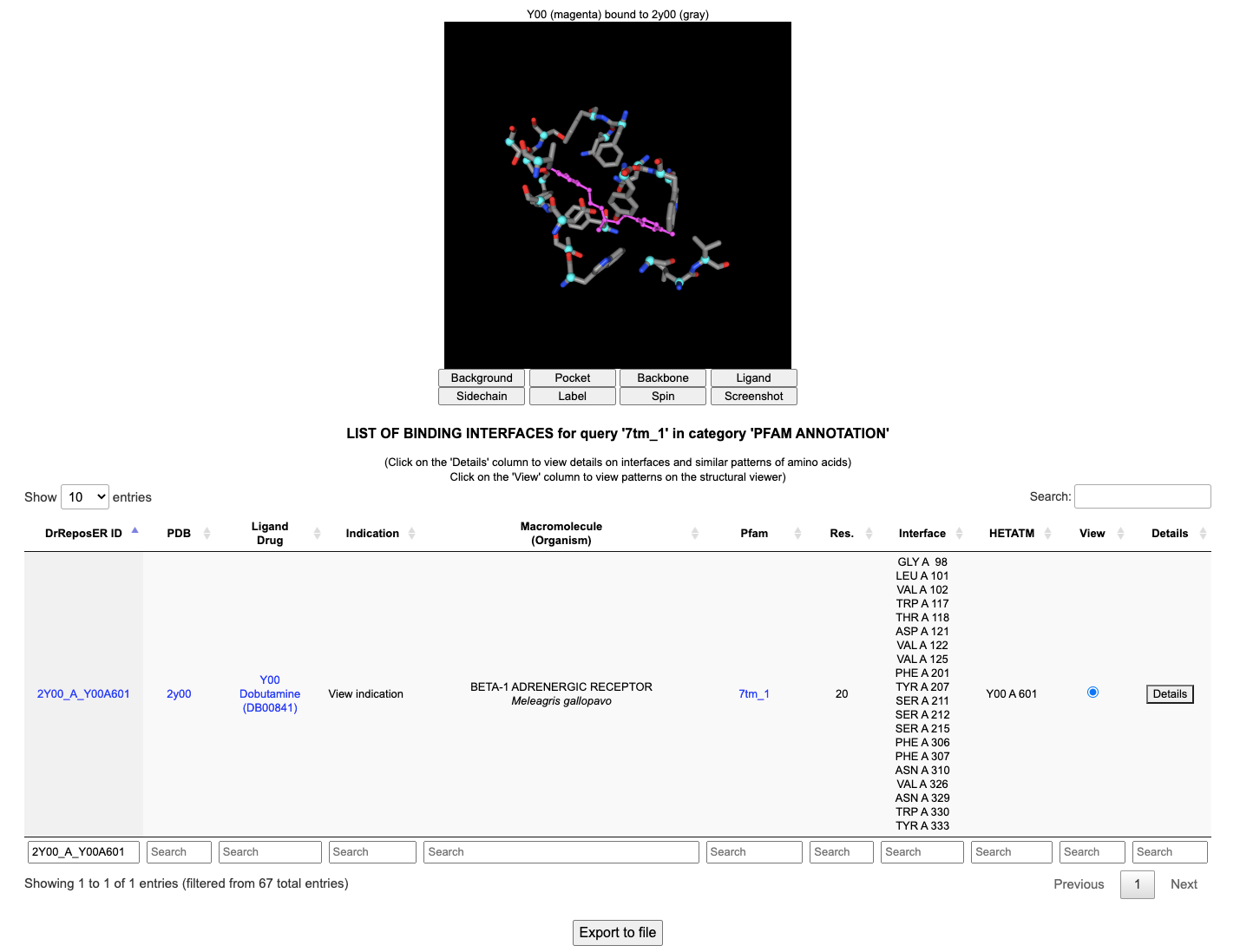
Clicking the radio on View column will open an NGL viewer that show the representation of selected binding site.
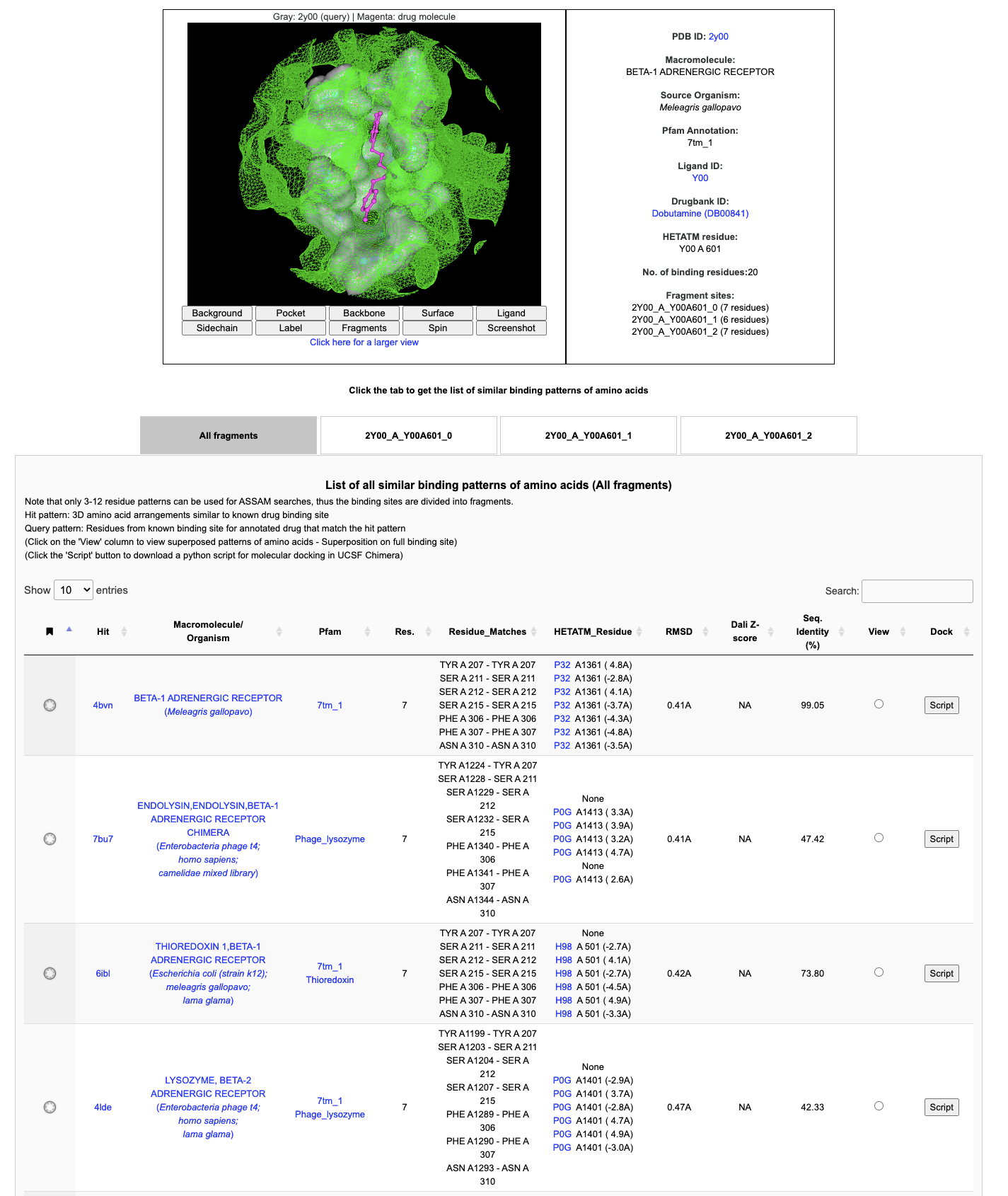
Clicking on the Details button, for example for the DrugReposER ID '2Y00_A_Y00A601', will open a new results page with a list of similar patterns of amino acids derived from ASSAM searches. Clicking the DrugBank ID or drug name will direct user to the DrugBank annotation, while clicking the PDB ID will direct user to PDBe for the selected protein. The Beta-1 Adrenergic receptor mediates the activation of adenylate cyclase through activities of G proteins upon binding of catecholamines such as adrenaline and noradrenaline. Other agonists such as dobutamine helps to stimulate the receptor to increase myocardial contractility and stroke volume and thus, increased cardiac output, which is useful for patients with heart diseases.
(Link)
1) Felix, A. K. & Overington, J. P. (2012). Global Analysis of Small Molecule Binding to Related Protein Targets. PLoS Comput Biol. 8(1):e1002333. (link)
2) Hauser et al. (2018). Pharmacogenomics of GPCR Drug Targets. Cell. 172(1-2):41-54. (link)
3) Sriram, K. & Insel, P. A. (2018). G Protein-Coupled Receptors as Targets for Approved Drugs: How Many Targets and How Many Drugs?. Mol Pharmacol. 93(4):251-258. (link)
4) Pfam annotation for 7 transmembrane receptor. (link)